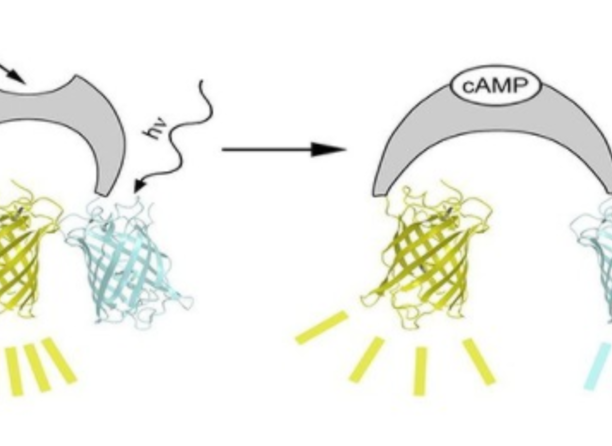
Cyclic AMP Biosensor - Genetically encoded FRET-based biosensor for cAMP
Ref.-Nr. F-0059
Keywords: Biosensor, cAMP, genetically encoded
Cyclic AMP is a key molecule in 2nd messenger cell signalling. Great effort has been taken to develop sensors that allow for noninvasive assessment of cAMP concentrations in living cells. Genetically encoded biosensors hold great promise to allow spatial and temporal measurements of cAMP concentrations in living cells. Yet, the sensors available up to now are hampered by the low affinity of the cAMP binding moieties employed. For example, the Epac-based sensors presented by Nikolaev et al. US 8889425 B2 bind cAMP with an affinity in the low mikromolar range, which may be insufficient for measuring basal cAMP levels. The inventors of the present invention identifed the cAMP nucleotide-binding domain of the bacterial MlotiK1 channel as superior cAMP sensing moiety for a FRET-based cAMP sensor. Sandwiched between a blue and a yellow fluorescent protein, this motif exhibits a nanomolar affinity and allows for real-time mesurement of intracellular cAMP concentration. The inventors were able to monitor the cAMP dynamics in different cell types, e.g. HEK293 cells, but also in flagella of sperm, thereby revealing the spatio-temporal distribution of cAMP controlling flagellar movement. This work, please find the reference below, proofs the applicability of the presented cAMP sensor for the investigation of cAMP-related biological questions.
Vorteile
- Nanomolar Affinity
- Fast binding/unbinding kinetics
- Expressed and purified in high amounts from prokaryotic cells
- Well expressed in eukaryotic cells
- Measurement of cAMP levels in solution in vitro, in cellulo, and in vivo
- No interaction with molecular pathways of eukaryotic cells
- Amenable to subcellular targeting
Kommerzielle Anwendung
The invention is available for licensing.
Aktueller Stand
The invention is described and claimed in the PCT application WO 2017/045970 A1 filed 09/06/2016. The national german counterpart DE 10 2015 115 640 B4 filed 09/16/2015 has been granted. This application is the priority application to said PCT application. The patent protects the use of a procaryotic cAMP nucleotide-binding domain for use in a biosensor.
Relevante Veröffentlichungen
Mukherjee et al.: eLife 2016;5:e14052 DOI: 10.7554/eLife.14052.